Industrial Valves: Design, Operation, and Safety Principles
Industrial valves are essential components in a wide array of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment. They regulate the flow, pressure, and direction of fluids, ensuring efficient and safe operations. This article delves into the design principles, operational mechanisms, and safety considerations of industrial valves.
What Are Industrial Valves?
Industrial valves are mechanical devices designed to control the flow and pressure of liquids, gases, or slurries within a system. Depending on their design and function, valves can start or stop flow, throttle or regulate it, or direct fluid in specific paths.
Types of Industrial Valves
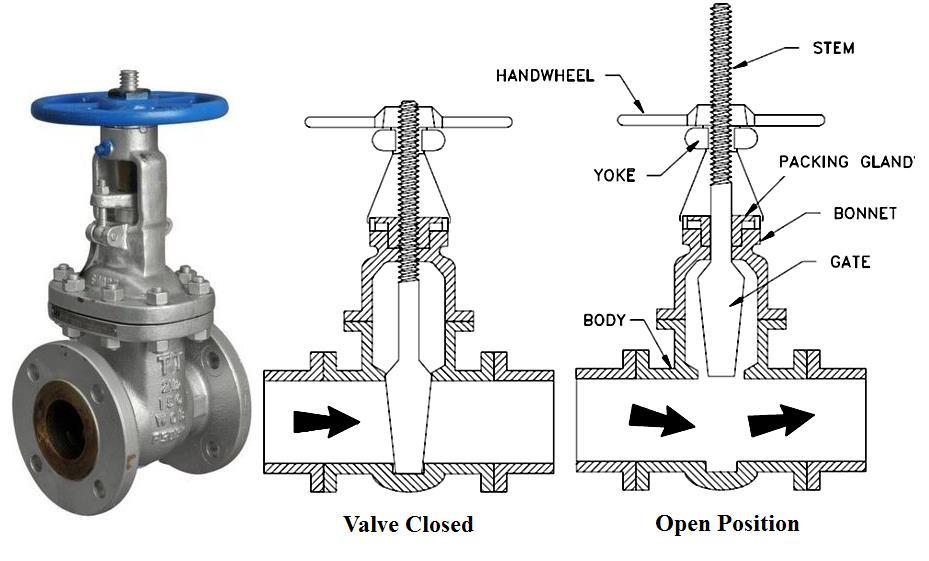
1. Gate Valves
- Design: Use a gate or wedge to control fluid flow.
- Operation: Provide a straight-through flow path with minimal pressure drop.
- Applications: Suitable for on/off control in pipelines.
- Advantages: Reliable sealing when fully closed.
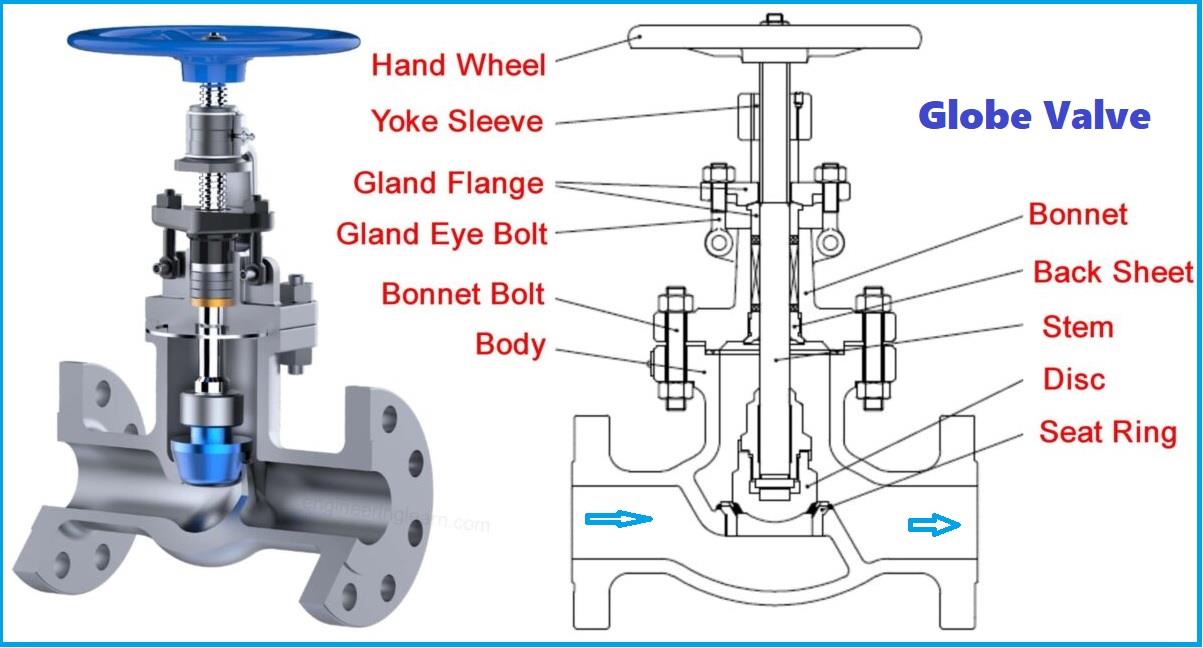
2. Globe Valves
- Design: Use a disk to throttle flow, moving perpendicularly to the seat.
- Operation: Offer precise flow control with higher pressure drops compared to gate valves.
- Applications: Ideal for systems requiring frequent throttling.
- Advantages: Excellent control and leak-tight sealing.
3. Ball Valves
- Design: Feature a rotating ball with a bore to control flow.
- Operation: Quick to open and close, providing full flow or shut-off.
- Applications: Widely used in industries needing tight shut-off and low-pressure drops.
- Advantages: Compact design with low maintenance.
4. Butterfly Valves
- Design: Utilize a rotating disk to regulate flow.
- Operation: Lightweight, cost-effective, and suitable for large-diameter applications.
- Applications: Common in water distribution and HVAC systems.
- Advantages: Quick operation and space-saving design.
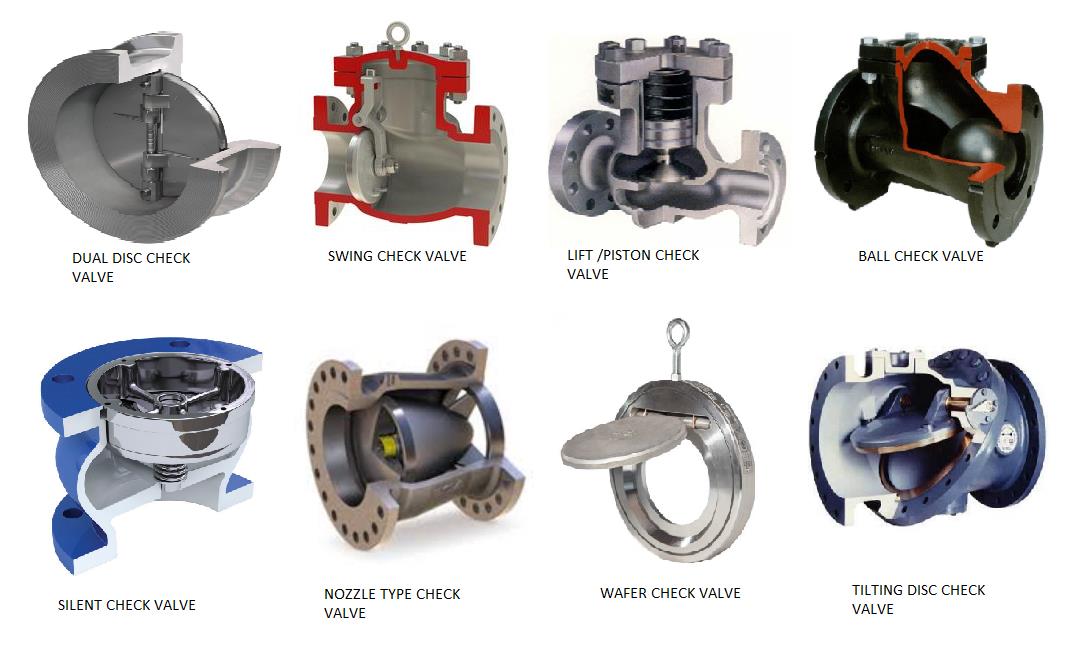
5. Check Valves
- Design: Prevent backflow using a flap, ball, or piston.
- Operation: Automatically operate based on pressure differences.
- Applications: Essential in pumps and compressors to avoid reverse flow.
- Advantages: Simple and reliable with minimal maintenance.

6. Pressure Relief Valves
- Design: Automatically release excess pressure to protect equipment.
- Operation: Open when the system pressure exceeds a set limit.
- Applications: Safety-critical systems like boilers and pressure vessels.
- Advantages: Prevent catastrophic failures due to overpressure.

Design Principles of Industrial Valves
1. Material Selection
- Criteria: Corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength.
- Common Materials: Stainless steel, cast iron, brass, and plastic for specific environments.
2. Flow Characteristics
- Linear: Flow rate changes proportionally with valve opening.
- Equal Percentage: Small openings cause minor flow changes, ideal for throttling.
- Quick-Opening: Rapid flow increase at the start, suitable for on/off applications.
3. Sealing Mechanisms
- Soft Seals: For low-pressure systems with minimal leakage tolerance.
- Metal Seals: For high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
4. Valve Sizing
- Importance: Oversized valves lead to poor control, while undersized ones cause pressure drops.
- Methodology: Based on system flow rate, pressure drop, and fluid properties.
Operation of Industrial Valves
- Manual Operation
- Using handwheels, levers, or gear mechanisms.
- Simple and cost-effective for low-frequency adjustments.
- Automatic Operation
- Actuators (electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic) control valves remotely or via automated systems.
- Ideal for precise and continuous operation in complex processes.
- Smart Valves
- Equipped with sensors and controls for real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
- Integrated into Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems for enhanced efficiency.
Safety Considerations for Industrial Valves
- Pressure Ratings
- Ensure valves can handle the maximum operating pressure without failure.
- Temperature Limits
- Select materials and seals that can withstand the system’s temperature range.
- Leak Prevention
- Use proper gaskets, packing, and regular maintenance to prevent hazardous leaks.
- Emergency Shut-Off Systems
- Install fail-safe valves to automatically close in critical conditions like pressure surges or fire.
- Regular Inspection and Testing
- Conduct periodic checks for wear, corrosion, and functionality.
- Adhere to industry standards like ASME, API, and ISO for valve testing.
Best Practices for Industrial Valve Maintenance
- Routine Cleaning
- Remove deposits and debris to prevent sticking or corrosion.
- Lubrication
- Regularly lubricate moving parts to reduce wear and ensure smooth operation.
- Seal Replacement
- Replace seals and packing materials during scheduled maintenance to avoid leaks.
- Calibration
- Verify valve settings, especially in throttling and control applications, for accurate operation.
- Documentation
- Maintain records of inspections, repairs, and replacements for compliance and troubleshooting.
Applications of Industrial Valves
- Oil and Gas: Flow control in pipelines and safety systems in refineries.
- Chemical Processing: Managing corrosive and hazardous fluids.
- Power Generation: Regulating steam and cooling water in thermal plants.
- Water Treatment: Controlling flow and pressure in filtration and distribution systems.
Conclusion
Industrial valves are indispensable for ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and safety of fluid handling systems. Understanding their design, operation, and maintenance can significantly enhance system performance and longevity. By adopting best practices and leveraging advanced technologies like smart valves, industries can optimize operations while adhering to strict safety standards. For expert guidance on valve selection, operation, or troubleshooting, consult an industrial valve specialist to tailor solutions to your specific needs.
 Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library
Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library







