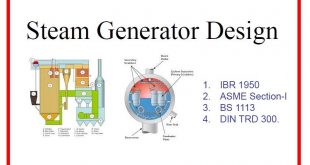
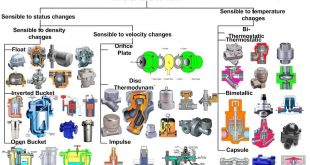
What is a Boiler?
The boiler is an important piece of equipment for most industrial facilities and power plants. The boiler is a closed pressure vessel in which water is converted into steam by the application of heat and used to produce high pressure or low-pressure steam or to produce hot water for industrial or domestic use. Usually, boilers are coal or oil-fired.
A boiler should fulfill the following requirements:
- Safety: The boiler should be safe under operating conditions.
- Accessibility: The various parts of the boiler should be accessible for repair and maintenance.
- Capacity: The boiler should be capable of supplying steam according to the requirements.
- Boiler Efficiency: To permit efficient operation, the boiler should be able to absorb a maximum amount of heat produced due to the burning of fuel in the furnace.

Industrial steam boilers are classified in too many ways.
Boiler Types According to tubing methods
The boilers can be classified according to the flow of water and hot gases, There are two major types of boilers Fire tube boilers and water tube boilers.
(a) Fire Tube
(b) Water Tube
Fire tube boilers are those boilers in which fire or flue gases are inside of the tubes and water is on the shell side. Fire Tube Boilers are low capacity low-pressure boilers usually used for heating, and processors to produce hot water.
The arrangement in the Water tube boiler water is that the water is contained inside the tubes while the hot combustion gas flows on the other side of the tubes. water tube boilers produce high-pressure steam which is used for power generation purposes. water tube boilers are more efficient and less dangerous than fire tube boilers. Mostly Fire tube boilers are Package type boilers that produce less amount and less pressure of steam than water tube boilers.
Boiler types According to the type of fuel used or fuel-burning methods
(a) Coal-fired boilers,
(b) Oil-fired boilers,
(c) Gas-fired boilers,
(d) Biomass boilers,
(e) Electric boilers
(f) Circulating Fluidized bed boiler(FBC Boiler),
(g) Pulverized coal boiler (PC Boiler), and
(h) Waste heat recovery boilers
(I) Nuclear Steam generators.
Boiler types According to steam Pressure
(a) Low-pressure Boilers
(b) Medium Pressure Boilers
(c) High-Pressure boilers.
According to ASME there every boiler have a pressure above 15 PSI is called a high-pressure boiler. but generally, Low-pressure boilers have pressure below 300 psi (Bulk Boiling). Medium pressure Boilers have a pressure range between 300 psi to 800 psi (mixed Nucleate or bulk Boiling). Boilers having Pressure above 800 psi (film Boiling) are called High-pressure Boilers.
According to the use of steam
Process boilers, Utility boilers, and Marine boilers are examples of these types of boilers.
If the steam is used for process the is called a process boiler. Utility boilers are used to generate electricity in power plants they are usually water tube type boilers.
According to the application of the Boiler:
(a) Stationary
(b) Mobile, (Marine, Locomotive).
Stationary and portable boilers, there are some boilers that are not stationary like Locomotive Boilers and Marine boilers.
According to the furnace position
Externally fired boilers and internally fired boilers. Some boilers have their furnace outside the boiler are called externally fired boilers. In internally fired boilers the grate combustion chamber is enclosed within the boiler shell whereas in the case of extremely fired boilers and furnace and grate are separated from the boiler shell.
- External Furnace
(a) Horizontal return tubular
(b) Short firebox
(c) Compact. - Internal Furnace
Horizontal Tubular
(a) Short firebox
(b) Locomotive
(c) Compact
(d) Scotch. - Vertical Tubular
(a) Straight vertical shell, vertical tube
(b) Cochran (vertical shell) horizontal tube.
According to the position of the principal axis :
(a) Vertical
(b) Horizontal
(c) Inclined.
Vertical and horizontal boilers. An example of a vertical boiler is the simple vertical boiler, Cochran boiler. Horizontal boilers are Cornish boiler, Lancashire boiler, and Locomotive Boiler
According to the No. of tubes in boilers
Single tube and multi-tube boilers. Single tube boilers like Cornish boiler and simple vertical boiler. These boilers have very low efficiency.
According to the circulation of water and steam in boilers
(a) Natural circulation
(b) Forced circulation.
Boilers are also classified as Natural circulation boilers and forced circulation boilers. The natural circulation limit is 140 Kg/cm2 above this pressure forced circulation is adopted.
According to the name of makers’ company names
Some companies make boilers like Babcock and Wilcox boilers and Cochran boilers. These boilers are famous for their brand names.
Water-tube boilers are usually classified as follows :
Horizontal Straight Tube Boilers
(a) Longitudinal drum
(b) Cross-drum.
Bent Tube Boilers
(a) Two drum
(b) Three drum
(c) Low head three drum
(d) Four drums.
Cyclone Fired Boilers
Cyclone furnace technology to burn coal grades that are not well-suited for pulverized coal combustion. The ash from these coals has a very low melting temperature. This molten ash would normally be deposited on all downstream heat transfer surfaces, causing severe slagging and fouling. Cyclone-fired boilers are known for their high efficiency and ability to burn a wide range of fuels, including coal, biomass, and waste materials. They are commonly used in power plants and industrial facilities.
 Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library
Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library