Bearings are mechanical components that reduce friction between moving parts and support loads. They come in various shapes and sizes, and each type has unique features and applications. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the most common types of bearings and their applications to help beginners understand their functions and uses.
-
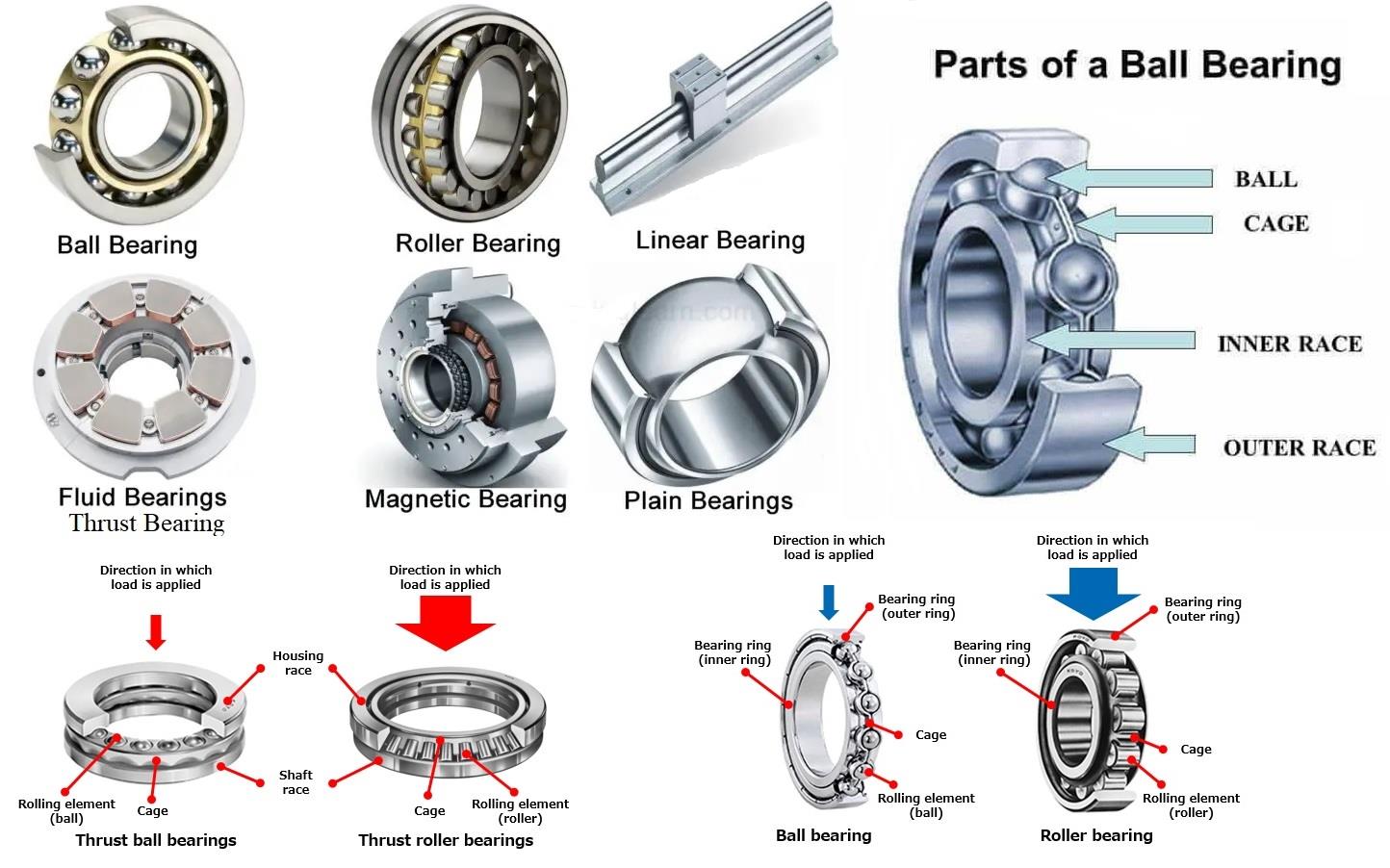
Ball Bearings:
Ball bearings are the most commonly used type of bearings. They consist of a series of small metal balls held in a ring-shaped track known as a raceway. Ball bearings reduce friction between two surfaces in contact and can handle both radial and thrust loads. They are used in various applications such as bicycles, electric motors, and conveyor systems.
Ball bearings consist of a series of small metal balls held in a ring-shaped track known as a raceway. The balls rotate between the inner and outer raceways, reducing friction and supporting loads. The balls are typically made of steel, but other materials such as ceramic, glass, and plastic are also used.
- Uses of ball bearing:
Ball bearings are used in various applications such as electric motors, pumps, conveyors, machine tools, and bicycles. They are also used in medical equipment, such as MRI machines and ultrasound equipment, as they provide smooth and low-friction motion.
- Advantages of ball Bearing:
Ball bearings offer several advantages, including:
- Low friction: Ball bearings reduce friction between two surfaces in contact, providing smooth and low-friction motion.
- High speed: Ball bearings can operate at high speeds without overheating, making them suitable for high-speed applications.
- Durability: Ball bearings are durable and can withstand high loads and extreme temperatures.
- Easy to maintain: Ball bearings require minimal maintenance, and the replacement of worn-out bearings is relatively easy.
- Types of Ball Bearing:
There are several types of ball bearings, including:
- Radial ball bearings: Radial ball bearings are the most common type of ball bearings. They are designed to handle radial loads, which are loads that act perpendicular to the shaft’s axis. Radial ball bearings can handle both light and heavy loads.
- Angular contact ball bearings: Angular contact ball bearings are designed to handle both radial and axial loads, which are loads that act parallel to the shaft’s axis. They are commonly used in automotive and aerospace applications.
- Self-aligning ball bearings: Self-aligning ball bearings are designed to compensate for shaft misalignment, making them suitable for applications that require high precision and accuracy.
- Thrust ball bearings: Thrust ball bearings are designed to support axial loads, which are loads that act parallel to the shaft’s axis. They are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications.
In conclusion, ball bearings are essential components in various mechanical systems, providing low friction, smooth motion, and load support. Understanding the different types of ball bearings and their applications is crucial to select the right bearing for specific needs.
-
Roller Bearings:
Roller bearings are similar to ball bearings but instead of balls, they have cylindrical rollers. They are used for heavy-duty applications that require higher load-carrying capacity. Roller bearings come in different types such as cylindrical, tapered, and spherical, and each has its specific uses. Cylindrical roller bearings are used in engines, while tapered roller bearings are used in automotive transmissions and axles.
Roller bearings consist of cylindrical or tapered rollers that are held in place by a cage. The rollers rotate between the inner and outer races, reducing friction and supporting loads. Roller bearings are designed to handle high radial and axial loads and are suitable for high-speed applications.
- Uses of Roller Bearing:
Roller bearings are used in various applications such as automotive transmissions, conveyor systems, wind turbines, printing presses, and mining equipment. They are also used in heavy machinery such as cranes, bulldozers, and excavators.
- Advantages of Roller Bearing:
Roller bearings offer several advantages, including:
- High load capacity: Roller bearings can support higher loads than ball bearings, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- High speed: Roller bearings can operate at high speeds without overheating, making them suitable for high-speed applications.
- Durability: Roller bearings are durable and can withstand high loads and extreme temperatures.
- Easy to maintain: Roller bearings require minimal maintenance, and the replacement of worn-out bearings is relatively easy.
Bearings Basic Concepts and Design Applications
- Types of Roller Bearing:
There are several types of roller bearings, including:
- Cylindrical roller bearings: Cylindrical roller bearings have cylindrical rollers and are suitable for high radial loads. They are commonly used in engines, transmissions, and power tools.
- Tapered roller bearings: Tapered roller bearings have tapered rollers and are suitable for both radial and axial loads. They are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications.
- Spherical roller bearings: Spherical roller bearings have barrel-shaped rollers and are suitable for high radial and axial loads. They are commonly used in heavy machineries, such as mining equipment and construction machinery.
- Needle roller bearings: Needle roller bearings have long, thin rollers and are suitable for high radial loads in limited space applications. They are commonly used in automotive and aerospace applications.
- Thrust roller bearings: Thrust roller bearings are designed to support axial loads, which are loads that act parallel to the shaft’s axis. They are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications.
-
Plain Bearings:
Plain bearings, also known as bushings, are simple bearings with a shaft rotating inside a sleeve. They are used to support loads and reduce friction between two surfaces in contact. Plain bearings come in various types such as sleeve bearings, flanged bearings, and thrust washers. They are used in various applications such as agricultural equipment, construction machinery, and hydraulic cylinders.
-
Thrust Bearings:
Thrust bearings are designed to support axial loads, which are loads that act parallel to the shaft’s axis. They are used in applications such as automotive transmissions, helicopter rotors, and machine tool spindles. Thrust bearings come in different types such as ball thrust bearings, cylindrical thrust bearings, and tapered roller thrust bearings.
Thrust bearings offer several advantages, including:
- High load capacity: Thrust bearings are designed to handle high axial loads and can support heavy loads without deformation or damage.
- Low friction: Thrust bearings reduce friction between two surfaces in contact, providing smooth and low-friction motion.
- Easy to install: Thrust bearings are relatively easy to install and require minimal maintenance.
- Durable: Thrust bearings are durable and can withstand high loads and extreme temperatures.
-
Magnetic Bearings:
Magnetic bearings use magnetic fields to support and control the motion of a rotating shaft without physical contact. They are used in applications that require high speed, accuracy, and low friction such as turbo machinery, high-speed trains, and flywheel energy storage systems.
Bearing Design in Machinery Engineering Tribology and Lubrication
-
Fluid Bearings:
Fluid bearings use a fluid layer to support and reduce friction between two surfaces in contact. They are used in applications that require high precision, low noise, and low vibration such as semiconductor manufacturing equipment, medical imaging machines, and precision measuring devices.
In conclusion, bearings play a vital role in various mechanical systems by reducing friction and supporting loads. Understanding the different types of bearings and their applications is essential for beginners to choose the right bearing for their specific needs.
 Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library
Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library





