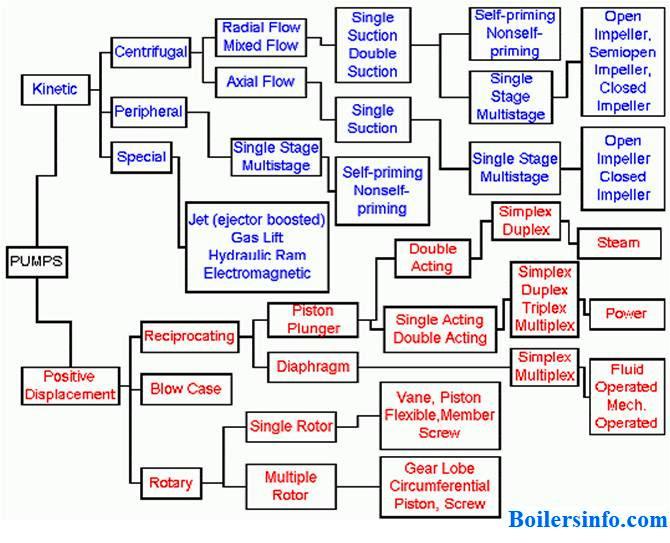
¨Pumps are divided into two fundamental types based on the manner in which they transmit energy to the pumped media: kinetic or positive displacement.
Kinetic Displacement Pumps, a centrifugal force of the rotating element, called an impeller, “impels” kinetic energy to the fluid, moving the fluid from pump suction to the discharge.
Positive Displacement Pumps use the reciprocating action of one or several pistons, or a squeezing action of meshing gears, lobes, or other moving bodies, to displace the fluid from one area into another (i.e., moving the material from suction to discharge).
Positive Displacement Pumps
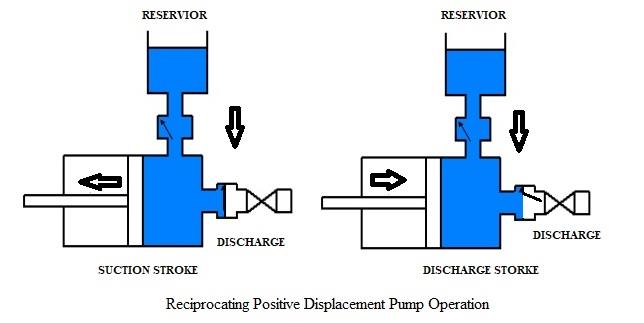
Reciprocating Pumps
Reciprocating pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that uses a back-and-forth (reciprocating) motion to transfer fluids. These pumps are known for their ability to provide precise and controllable flow rates, making them suitable for applications where accuracy is crucial. They are used in a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and more.
Rotary Pumps
Rotary pumps function by trapping fluid between rotating components and the pump casing. This type includes gear pumps, vane pumps, and lobe pumps. Rotary pumps are known for their consistent flow rates and self-priming capabilities.
Dynamic Pumps
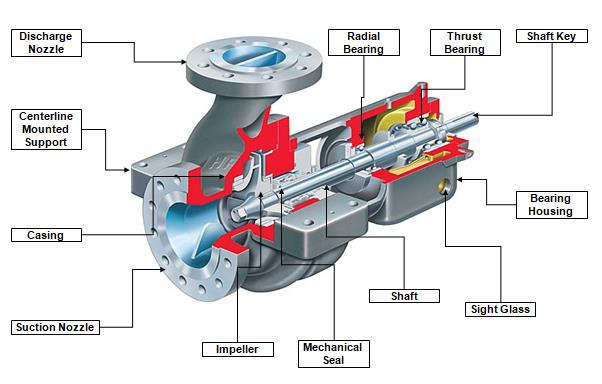
Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in various industries due to their simplicity and efficiency. They work by converting rotational energy into kinetic energy, creating a flow within the pump casing. They are suitable for moving large volumes of fluids at moderate pressures. Also, read Centrifugal Pump Classification Widely used in industry.
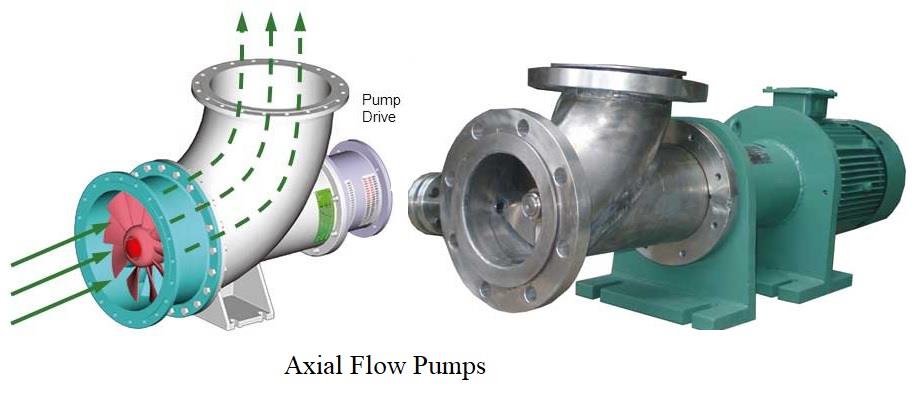
Axial Flow Pumps
Axial flow pumps are a type of centrifugal pump used to transport fluids, typically liquids, by generating an axial flow pattern. In contrast to radial flow pumps, which push fluid outward from the center of the impeller, axial flow pumps move fluid parallel to the pump shaft. These pumps are particularly well-suited for applications requiring high flow rates and relatively low heads (pressure).
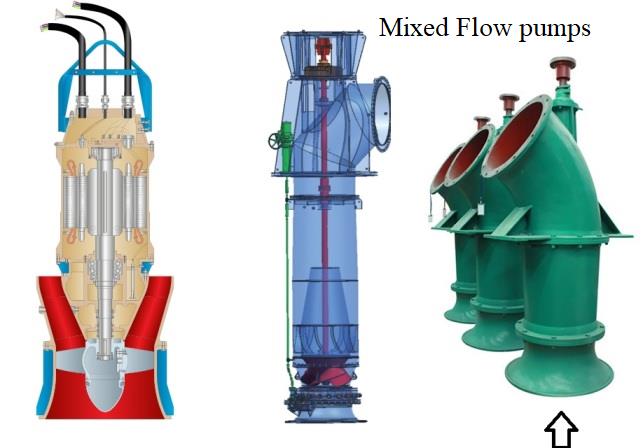
Mixed Flow Pumps
Mixed flow pumps are a type of centrifugal pump commonly used for pumping water and other fluids. They combine features of both radial flow (centrifugal) and axial flow pumps, hence the name “mixed flow.” These pumps are designed to handle moderate to high flow rates at medium to high pressures.
Specialized Pumps
Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps utilize a flexible diaphragm to create a vacuum, drawing in and expelling fluid. These pumps are often used for corrosive or abrasive fluids and in applications requiring precise metering. Diaphragm pumps, also known as membrane pumps, are a type of positive displacement pump that uses a flexible diaphragm to move fluid. These pumps are known for their versatility, ability to handle a wide range of fluids, and suitability for various applications, including those involving viscous, abrasive, corrosive, and shear-sensitive liquids.
Peristaltic Pumps
Peristaltic pumps use rotating rollers to compress a flexible tube, propelling the fluid within. They are suitable for hygienic applications, laboratory use, and situations where cross-contamination must be avoided.
Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that use rotating gears to transfer fluids. They are commonly used for pumping a wide range of liquids, from low-viscosity to high-viscosity fluids, and are known for their efficiency, simplicity, and reliability. Gear pumps can be found in various industries, including automotive, chemical, oil and gas, and food processing. Gear pumps are positive displacement pumps, meaning they move a fixed volume of fluid with each rotation of the gears. This results in a consistent flow rate regardless of changes in pressure.
Jet Pumps
Jet pumps operate using a jet of high-speed fluid to create a vacuum, drawing in the desired fluid. They are often used for domestic water supply and oil wells.
Comparison of Pump Types
Choosing the right pump type depends on various factors such as flow rate, pressure, viscosity, and the nature of the fluid being pumped. Positive displacement pumps are suitable for accurate metering, while dynamic pumps are better for high-flow, low-pressure situations.
Factors Influencing Pump Selection
When selecting a pump, consider factors like fluid properties, desired flow rate, pressure requirements, and operational efficiency. It’s crucial to match the pump’s capabilities with the specific application to ensure optimal performance.
Maintenance and Efficiency Tips
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of pumps. Regular inspections, lubrication, and monitoring of vibration and noise levels can help identify issues early and prevent costly breakdowns.
Importance of Proper Pump Selection
Selecting the right pump type and size is crucial for efficient operation and energy savings. A well-chosen pump can lead to reduced maintenance costs, improved productivity, and decreased downtime.
FAQs
Q1: Can centrifugal pumps handle high-viscosity fluids?
Centrifugal pumps are better suited for low-viscosity fluids. For high-viscosity liquids, positive displacement pumps like gear pumps are more appropriate.
Q2: Are axial flow pumps suitable for high-pressure applications?
No, axial flow pumps are designed for low to moderate pressures and are better suited for applications requiring high flow rates.
Q3: What are the advantages of peristaltic pumps?
Peristaltic pumps offer gentle pumping action, making them suitable for shear-sensitive fluids and applications requiring precise dosing.
Q4: Can I use a centrifugal pump for industrial chemical transfer?
Yes, centrifugal pumps can handle a variety of chemicals, but it’s essential to select materials that are compatible with the specific chemicals being pumped.
Q5: How can I improve the efficiency of my pump system?
Regular maintenance, proper pump sizing, and optimizing the system’s piping layout can contribute to improved pump efficiency.
In conclusion, pumps are essential devices with diverse applications across industries. Understanding the classification and types of pumps allows for informed decisions when selecting the right pump for specific needs. Proper maintenance and consideration of key factors during selection can lead to efficient and reliable pump operations.
 Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library
Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library