How to Use Automotive Diagnostic Scanners
Automotive diagnostic scanners are invaluable tools for understanding and resolving vehicle issues. They’ve evolved significantly since the advent of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD), which emerged in the late 1980s to monitor emissions and engine performance. The introduction of OBD-II in 1996 standardized diagnostic systems across all vehicles, enabling universal access to emissions-related data. This evolution supports key components like catalytic converters, oxygen sensors, and electronic fuel delivery systems.
Table of Contents
ToggleA Brief Overview of Diagnostic Scanners
Modern diagnostic scanners, including professional scanners and code readers, offer varying capabilities. Simple code readers display Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), while advanced scan tools provide real-time data streams, component tests, and bidirectional control for comprehensive analysis.
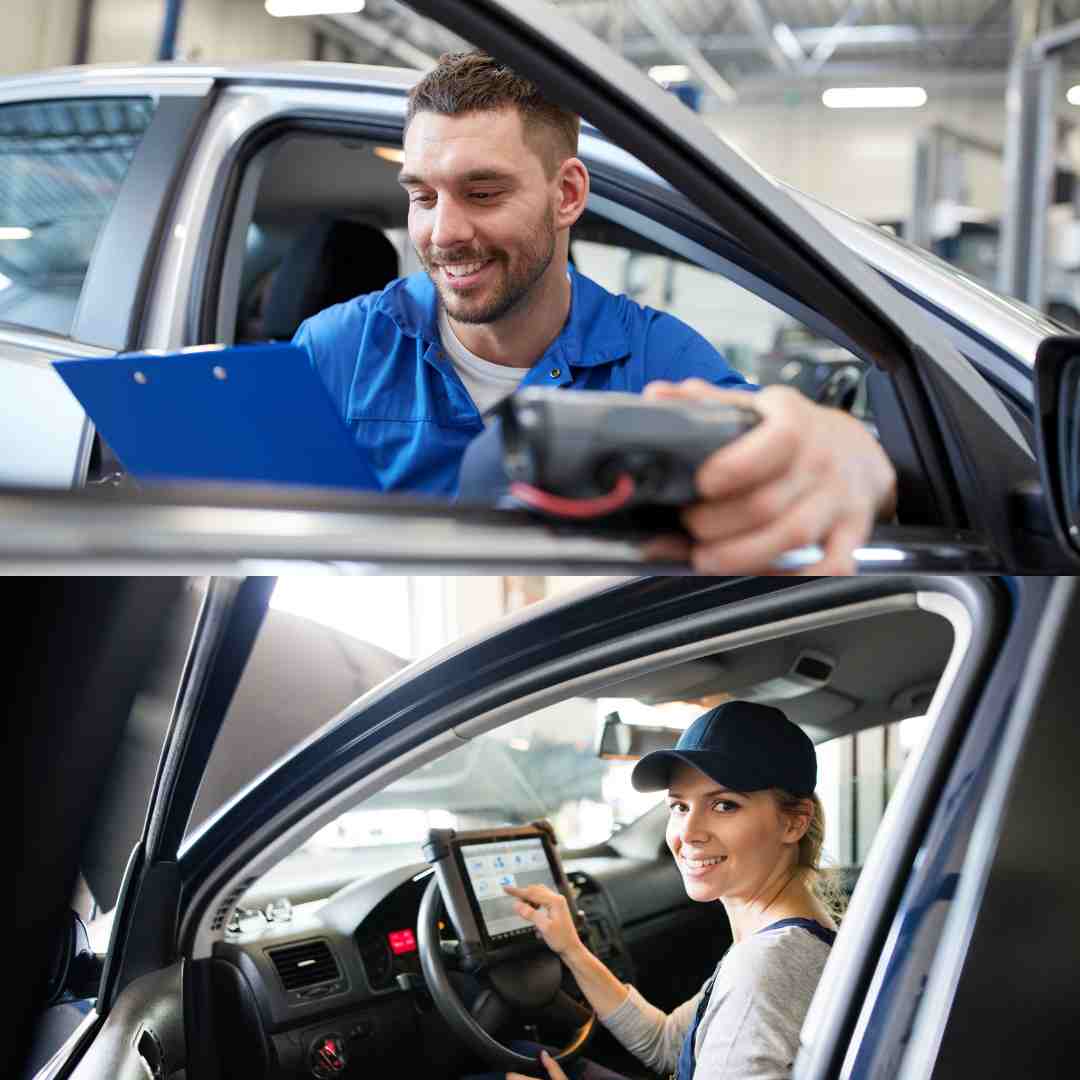

How to Operate a Scanner
1. Connect the Scanner
Plug the scanner into the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard near the driver’s seat.
2. Power On
Turn the vehicle’s ignition to “ON” without starting the engine. Most scanners automatically power up, though some require manual activation.
3. Access Vehicle Information
Modern scanners may detect the vehicle’s make, model, and year automatically. Otherwise, enter this information manually.
4. Retrieve and Interpret Codes
Navigate to the diagnostics menu to retrieve trouble codes. Common codes often relate to emission components, like the catalytic converter or oxygen sensors. Use built-in or external resources to interpret codes accurately.
5. Analyze Data and Perform Tests
Advanced scanners can monitor real-time data, such as fuel trim or airflow, helping to pinpoint faults. These tools are vital for detailed automotive detective work.
6. Clear Codes and Reset
Once repairs are completed, use the scanner to clear codes and reset the Check Engine light.
Latest Scanner Models
Modern automotive diagnostic scanners have evolved to meet the demands of increasingly complex vehicle systems. These tools now come equipped with a range of advanced features designed to enhance their functionality and user experience:
Wireless Connectivity
Many scanners now support Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connections, allowing seamless communication with mobile devices or computers. This eliminates the need for physical cables, making diagnostics more convenient.
Smartphone and Tablet Apps
Scanners like the BlueDriver OBD2 and similar models pair with smartphone apps, offering intuitive interfaces and expanded capabilities. These apps often include diagnostic code libraries, real-time data visualization, and step-by-step repair guides.
Enhanced Compatibility for Hybrid and EVs
As hybrid and electric vehicles become more popular, scanners like the Autel MaxiSYS Ultra offer specialized functions for diagnosing electric drive systems, high-voltage batteries, and regenerative braking components.
Cloud Integration and Updates
The latest models, such as the Launch X431 V+, support cloud storage for diagnostic data and automatic software updates, ensuring they remain compatible with the newest vehicle models and systems.
Advanced Bi-Directional Control
High-end scanners like the Snap-on Solus Edge enable technicians to perform bi-directional tests, controlling components such as fuel pumps, injectors, and throttle actuators directly through the scanner.
User-Friendly Touchscreen Interfaces
Many scanners now feature large, high-resolution touchscreens, making them easier to navigate and operate. These devices often come preloaded with detailed databases of diagnostic codes and repair procedures.
Multilingual Support
To cater to global users, modern scanners provide multilingual interfaces, expanding their accessibility and usability across diverse regions.
Advanced Features of Modern Scanners
The latest automotive diagnostic scanners are equipped with state-of-the-art features that go beyond simple code reading. These include:
Wireless and Bluetooth Connectivity
Many scanners now connect via Bluetooth to smartphones or tablets, enabling diagnostics through dedicated mobile apps. This adds portability and user-friendly interfaces to the diagnostic process.
Real-Time Data Monitoring
Advanced scanners provide live data streams, such as engine speed, temperature, and fuel efficiency. This feature allows technicians to observe how the vehicle performs under different conditions.
Bi-Directional Control
High-end scan tools enable users to send commands to specific vehicle components, such as activating fuel pumps or testing ABS systems, making them essential for in-depth diagnostics and repairs.
Hybrid and EV Compatibility
With the rise of hybrid and electric vehicles, scanners now support diagnostic functions specific to these systems, such as monitoring battery health and high-voltage systems.
Enhanced User Interface and Updates
Many tools feature intuitive touchscreens and automatic software updates, ensuring compatibility with new vehicle models and improved functionality.
A Case for Professional Scanners
While basic code readers are accessible to casual users, professional-grade scanners are indispensable for mechanics and technicians. These devices provide deeper insights into vehicle systems, including transmission diagnostics, advanced emissions monitoring, and safety systems like airbags and stability control.
Using Scanners for Automotive Detective Work
Diagnostic scanners are invaluable for uncovering the root causes of vehicle issues. When used in combination with technical knowledge, they can help diagnose complex problems related to:
- Electronic fuel delivery systems: Monitor fuel injection performance and pressure levels.
- Catalytic converters and oxygen sensors: Identify inefficiencies or failures in emissions control.
- Drivability issues: Analyze engine misfires, air intake problems, or transmission faults.
Conclusion
Understanding how to use an automotive diagnostic scanner is a skill that can save time and money while ensuring the longevity of your vehicle. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional technician, mastering these tools opens up a world of possibilities in vehicle maintenance and repair. With modern scanners offering advanced capabilities like real-time monitoring, bidirectional control, and hybrid/EV support, staying ahead in automotive diagnostics has never been easier.
 Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library
Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library