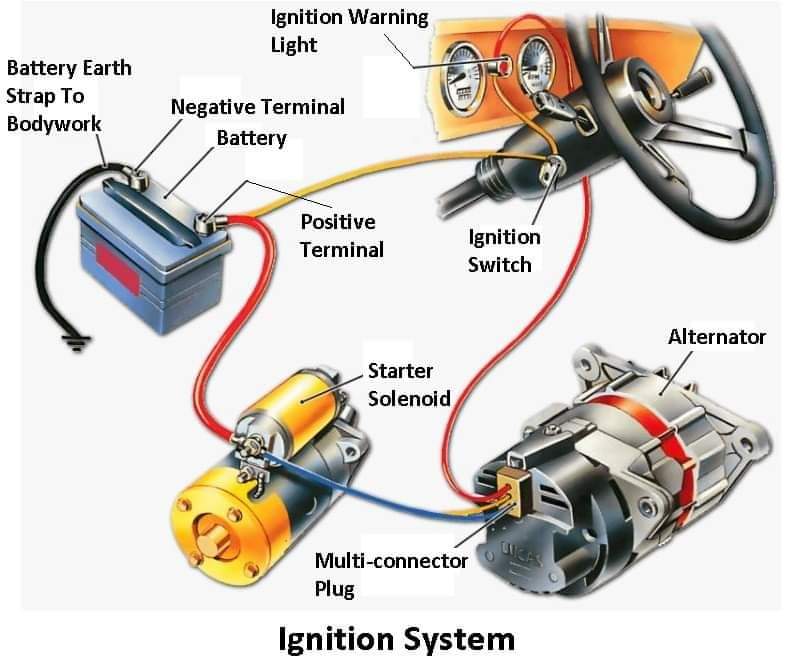
The Role of the Ignition System in Automobiles
The ignition system is an essential component in every gasoline-powered automobile. It is responsible for initiating the combustion process within the engine, providing the necessary spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture. Understanding how the ignition system works and its different components is crucial to maintaining a vehicle’s performance and ensuring smooth operation.
Key Components of the Ignition System
Spark Plugs
At the heart of the ignition system are the spark plugs. These small, yet vital components generate the electrical spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture within the engine’s combustion chamber. Spark plugs are placed at specific intervals along the cylinder head and require a precise electrical charge to produce a powerful spark.
Ignition Coils
Ignition coils are responsible for transforming the low voltage from the battery into a high-voltage surge, which is essential for creating a strong spark at the spark plugs. Modern automobiles often have individual ignition coils for each cylinder, while older models may have a single coil supplying multiple spark plugs.
Distributor (Older Systems)
In older vehicles with conventional ignition systems, a distributor is used to route the high-voltage current from the ignition coil to each spark plug. The distributor rotates, sending the electric charge to the correct spark plug at the right time, ensuring precise ignition timing for each cylinder.
The Ignition Process
The ignition process starts when the driver turns the key or presses the engine start button. This action triggers a series of events within the ignition system:
1. Battery Power
When the ignition key is turned, power from the vehicle’s battery is sent to the ignition coil, which then transforms it into a high-voltage charge.
2. Ignition Coil
The ignition coil converts the low-voltage electricity from the battery into a high-voltage surge, capable of producing a strong spark.
3. Spark Plugs
The spark plugs receive the high-voltage charge from the ignition coil and generate a spark across the spark plug gap, igniting the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
4. Combustion
The ignited air-fuel mixture rapidly expands, creating a high-pressure force that pushes the piston down the cylinder. This mechanical energy is then converted into rotational motion, which drives the vehicle’s wheels.
Types of Ignition Systems
Conventional Ignition System
Older vehicles typically use a conventional ignition system with a distributor, ignition coil, and spark plugs. While reliable, these systems require more maintenance and can be less efficient than modern alternatives.
Electronic Ignition System
Modern automobiles are equipped with electronic ignition systems, which have eliminated the need for a distributor. Instead, individual ignition coils for each cylinder and an engine control module (ECM) manage the ignition timing. Electronic ignition systems offer improved reliability, efficiency, and better control over ignition timing.
Conclusion
The ignition system is a fundamental part of every gasoline-powered automobile, enabling the engine to start and function efficiently. Regular maintenance of the spark plugs, ignition coils, and related components is essential for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. As automotive technology continues to advance, electronic ignition systems have become the norm, further improving vehicle reliability and overall performance. Understanding the role of the ignition system empowers drivers to appreciate their vehicles’ inner workings and make informed decisions when it comes to maintenance and repairs.
 Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library
Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library