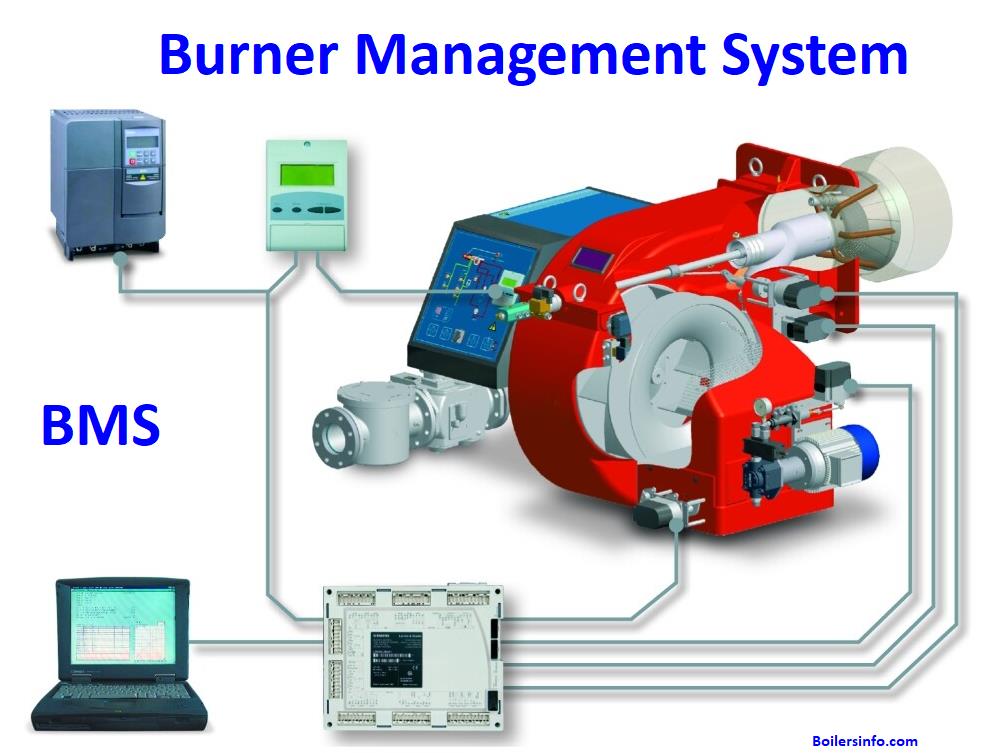
A burner management system (BMS) is a control system that is used to monitor and regulate the operation of burners in industrial processes such as Boilers, power plants, chemical plants, and oil refineries. The BMS is responsible for ensuring that the burners are operating safely and efficiently, and it can be used to monitor a variety of parameters, including fuel flow, oxygen levels, temperature, and pressure. The BMS can be programmed to automatically adjust the operation of the burners in response to changes in these parameters or in response to signals from other control systems. It can also be used to shut down the burners in the event of an emergency or malfunction.
A burner management system (BMS) typically includes the following components:
- Sensors: These are used to measure various parameters of the burners and the surrounding environment, such as fuel flow, oxygen levels, temperature, and pressure.
- Control panel: This is the central hub of the BMS, where all of the sensor data is collected and processed. It typically includes a display screen that shows the status of the burners and any alarms that have been triggered.
- Control logic: This is the software that runs on the control panel and determines how the BMS should respond to changes in sensor data. It may include pre-programmed rules for adjusting the operation of the burners, as well as algorithms for analyzing sensor data and identifying patterns or trends.
- Actuators: These are devices that are used to control the operation of the burners, such as valves and dampers. The BMS sends signals to the actuators to adjust the flow of fuel or air to the burners as needed.
- Communication interfaces: These allow the BMS to communicate with other control systems or devices, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- Safety shutdown devices: These are used to automatically shut down the burners in the event of an emergency or malfunction. They may include pressure switches, temperature switches, or flame detectors.
Safety features and measures for the burner management system (BMS)
- Sensors: The BMS uses sensors to monitor various parameters of the burners and the surrounding environment, such as fuel flow, oxygen levels, temperature, and pressure. If any of these parameters go outside of safe limits, the BMS can trigger an alarm or automatically shut down the burners to prevent accidents or damage.
- Control logic: The BMS includes software that analyzes sensor data and determines how the burners should be adjusted to maintain safe and efficient operation. This may include pre-programmed rules for adjusting the burners in response to changes in sensor data, as well as algorithms for identifying patterns or trends that could indicate a potential problem.
- Safety shutdown devices: The BMS may include pressure switches, temperature switches, or flame detectors that are designed to automatically shut down the burners in the event of an emergency or malfunction.
- Communication interfaces: The BMS may be connected to other control systems or devices, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, which can provide additional layers of safety and monitoring.
- Operator training: Proper operator training is also important for ensuring the safe operation of a BMS. Operators should be familiar with the BMS system and its safety features, and they should be trained in how to respond to alarms or other indications of a potential problem.
 Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library
Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library