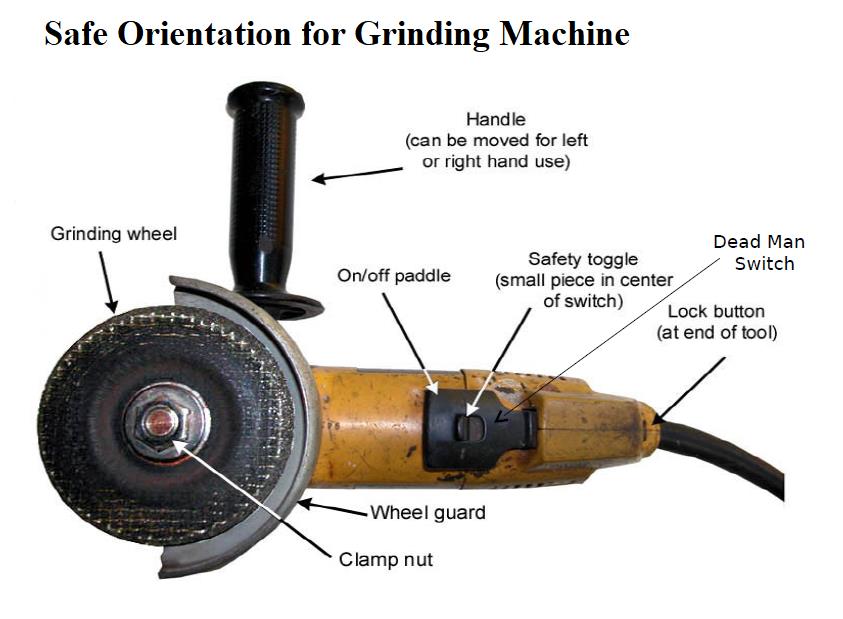
Grinding in its various forms is a vital part of many processes. It involves a cutting process that utilizes sharp abrasive grains bonded together in the form of a grinding wheel or disk. In this article, we will explore the different types of grinders, potential hazards associated with grinding operations, the importance of planning and assessment, safe work practices, and the reporting of faults or hazards.
Introduction
Grinding is a fundamental process that is used in various industries to shape and finish workpieces. It involves the removal of material from a surface using abrasive grains, which are typically bonded together to form a grinding wheel or disk. This process is crucial for achieving precise dimensions, improving surface finish, and preparing workpieces for further operations.
Types of Grinders
Grinding equipment comes in various forms to suit different applications. Here are some common types of grinders that you may encounter:
1. Portable Handheld Grinders (Air and Electrically Driven)
Portable handheld grinders are versatile tools that can be easily carried and used for grinding operations in different locations. They are available in both air-driven and electrically driven versions, providing flexibility based on the available power source.
2. Pedestal Grinders
Pedestal grinders are larger stationary grinders mounted on a pedestal or a bench. They offer stability and precision for heavier grinding tasks and are commonly found in workshops and manufacturing facilities.
3. Precision Grinders
Precision grinders, such as surface grinders and cylindrical grinders, are specialized machines used for achieving high accuracy and surface finish. Surface grinders are used to create flat surfaces, while cylindrical grinders are used for cylindrical or round workpieces.
Hazards Associated with Grinding
Grinders and grinding operations pose several hazards that need to be considered for a safe working environment. Here are some common hazards associated with grinding:
1. Cuts and Abrasions
Contact with the rotating wheel or disk can result in cuts and abrasions. The sharp edges of the abrasive grains can cause injuries if proper precautions are not taken.
2. Hearing Loss
Excessive noise generated during grinding operations can lead to hearing loss if suitable hearing protection is not worn. The Constant exposure to loud grinding noises can have long-term effects on hearing health.
3. Shattering or Explosion
Disks or wheels used in grinding machines can shatter or explode if they are not properly maintained or if they are subjected to excessive force or stress. This can pose a significant risk to the operator and others nearby.
4. Eye Injuries
Particles generated during grinding operations can be propelled at high velocities, causing eye injuries. It is crucial to wear appropriate eye protection to shield against flying debris.
5. Manual Handling Injuries
Controlling the forces generated by the grinding process and maintaining the correct workplace posture can lead to manual handling injuries if proper techniques and ergonomics are not followed.
Planning and Assessment
Before commencing any grinding job or using grinding equipment, it is essential to take necessary precautions to ensure safety. The following factors should be considered during the planning and assessment phase:
1. Selecting the Correct Wheel
Choosing the right grinding wheel for the job is crucial. Different materials and applications require specific types of wheels to ensure optimal performance and safety. Check the expiry date.
2. Equipment Inspection
Thoroughly inspect the grinders and ensure they are in good condition before use. Check for any damage, ensure guards are fitted, and verify the integrity of electrical leads. Proper tagging and maintenance of equipment are essential.
3. Adequate Lighting
Ensure that the work area has sufficient lighting so that you can clearly see the task at hand. Proper illumination is crucial for maintaining accuracy and preventing accidents.
4. Work Area Setup
Set up the work area in a way that allows easy access without overreaching. Avoid strains and sprains by ensuring that the workpiece is within comfortable reach.
5. General Housekeeping
Maintaining a tidy work area is essential for safety. Untidy work areas can contribute to accidents, and failure to clean up dust or grinding can increase the risk of eye injuries.
Safe Work Practices
To ensure safety during grinding operations, it is important to follow safe work practices. Here are some key points to remember:
- Always wear safety glasses and a full clear face shield, as a minimum. Consider using full-sealing mono goggles for added protection.
- Warn personnel in your work area before starting grinding operations. This gives them the chance to protect themselves by wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Inspect grinding wheels before each use, especially portable grinders that are prone to physical damage. Replace damaged or worn-out wheels promptly.
- Ensure grinding wheels have been correctly fitted using the appropriate collars and flanges. Avoid side-loading cutting wheels, as they may shatter.
- Use aluminum only on correct grinding wheels to prevent any chemical reactions or hazards.
- Start grinding gently and avoid overloading the wheel or grinder. Excessive pressure can lead to wheel breakage and potential injuries.
- Use suction devices or extraction ventilation to remove grinding fumes and dust from the work area. Proper ventilation helps maintain a clean and healthy environment.
- Secure the object being ground firmly whenever possible. Avoid “live” grinding where the workpiece can freely move about, as it reduces noise and minimizes the chance of accidents.
- Always wear hearing protection, such as ear muffs or earplugs, when engaged in grinding activities. Protecting your hearing is crucial for long-term health.
- Clean up dust and grindings as part of the job to reduce the chance of eye injuries. Proper disposal of debris and waste contributes to a safer work environment.
Reporting of Faults/Hazards
Identifying and addressing hazards promptly is essential for maintaining a safe workplace. If you come across any unsafe situations or faults, follow these steps:
- If possible, fix the problem yourself, taking appropriate safety measures.
- If you cannot fix the issue, make sure to isolate the hazard and report it to your supervisor immediately.
- Your supervisor will take the necessary actions to remedy the situation and ensure the safety of all personnel.
- Incident Accident and Reporting of Near Misses
Conclusion
Grinding is a critical process utilized in various industries, but it also comes with potential hazards. By understanding the types of grinders, assessing the risks, and following safe work practices, we can minimize the chances of accidents and ensure a safe working environment. Remember to prioritize safety, wear appropriate protective equipment, and report any faults or hazards promptly.
 Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library
Boilersinfo Boiler and Mechanical Power Digital Library